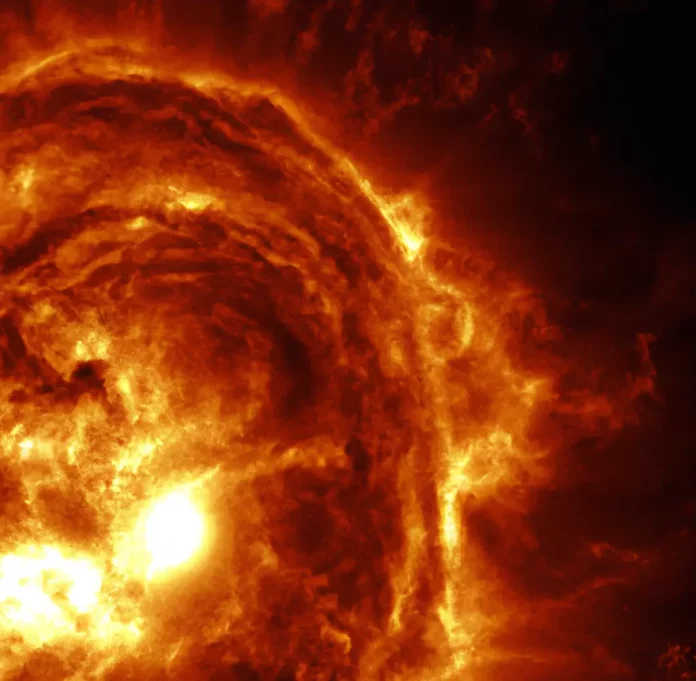
Solar Electromagnetic Pulse (SEMP) is a phenomenon that can affect electronic devices and power grids on Earth. It is a type of electromagnetic pulse (EMP) that is generated by solar flares and coronal mass ejections. In this article, we will explore the science behind SEMP and its effects on technology.
Table of Contents
- What is a Solar Electromagnetic Pulse?
- How is SEMP generated?
- Effects of SEMP on Electronic Equipment
- Protection Against SEMP
- Applications of SEMP
- Risks and Dangers of SEMP
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is a Solar Electromagnetic Pulse?
A Solar Electromagnetic Pulse (SEMP) is a burst of electromagnetic radiation caused by solar flares and coronal mass ejections. These events release a large amount of energy in the form of charged particles, which can affect electronic devices and power grids on Earth.
How is SEMP generated?
SEMP is generated by solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Solar flares are sudden releases of energy from the Sun’s atmosphere, while coronal mass ejections are large eruptions of plasma and magnetic fields from the Sun’s corona. These events release a large amount of charged particles, which can interact with the Earth’s magnetic field and create a rapidly changing electromagnetic field.
 Effects of SEMP on Electronic Equipment
Effects of SEMP on Electronic Equipment
SEMP can cause significant damage to electronic equipment, including communication devices, power grids, and satellites. The effects of SEMP on electronic devices are caused by the rapid change in electromagnetic fields, which can induce high voltages in conductive materials. This can cause electronic devices to fail or malfunction.
Protection Against SEMP
There are several ways to protect against SEMP. One way is to shield electronic devices from the electromagnetic pulse using conductive materials, such as metal or carbon fiber. Another way is to design electronic devices to be resistant to electromagnetic interference. This can be done by using components that are less sensitive to electromagnetic fields, such as ceramic capacitors or thick-film resistors.
Applications of SEMP
SEMP has several applications, including in scientific research and space exploration. SEMP can be used to study the Sun’s activity and its effects on Earth. It can also be used to test the resilience of electronic equipment in extreme conditions.
Risks and Dangers of SEMP
SEMP poses a significant risk to electronic equipment, which can lead to the failure of critical systems, such as power grids and communication networks. The effects of SEMP can also be long-lasting, as electronic devices may need to be repaired or replaced. Additionally, the impact of SEMP on space-based assets, such as satellites, can have severe consequences for communication and navigation systems.
Conclusion
Solar Electromagnetic Pulse is a phenomenon that can affect electronic devices and power grids on Earth. It is generated by solar flares and coronal mass ejections, and its effects can be significant. Protecting electronic devices from SEMP is important, as it can cause critical systems to fail. It is also important to consider the risks and dangers associated with the impact of SEMP on space-based assets.
FAQs
- Can SEMP affect humans directly? No, SEMP cannot affect humans directly. However, the effects of SEMP on electronic devices can indirectly impact human lives.
- Can electronic devices be protected from SEMP? Yes, electronic devices can be protected from SEMP by shielding them from the electromagnetic pulse or designing them to be resistant to electromagnetic interference.
- Can SEMP cause power outages? Yes, SEMP can cause power outages by damaging power grids and electronic equipment.
- How often do solar flares and coronal mass ejections occur? Solar flares and coronal mass ejections occur regularly, but their frequency and intensity can vary.
- Can SEMP be predicted? SEMP can be predicted to some extent by monitoring the activity of the Sun. However, predicting the exact timing and intensity of a SEMP event is still a challenge for scientists.